 SAFOD (San Andreas
Fault Observatory at Depth)
SAFOD (San Andreas
Fault Observatory at Depth)
SAFOD is a
4-km-deep observatory drilled directly into the San Andreas fault zone
near the nucleation point of the 1966 magnitude 6 Parkfield earthquake.
The project will reveal the physical and chemical processes acting deep
within a seismically active fault. Initially, fault-zone rocks and fluids
will be retrieved for laboratory analyses, and intensive downhole
geophysical measurements will be taken within and adjacent to the active
fault zone. The observatory’s long-term monitoring activities will include
decades of detailed seismological observations of small- to moderate-sized
earthquakes, and continuous measurement of pore pressure, temperature and
strain during the earthquake cycle. SAFOD will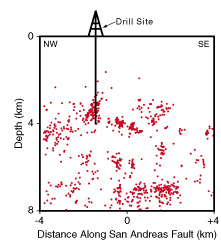 provide direct
information on the composition and mechanical properties of faulted rocks,
the nature of stresses responsible for earthquakes, the role of fluids in
controlling faulting and earthquake recurrence and the physics of
earthquake initiation and growth. Drilling, sampling, downhole
measurements and long-term moni- toring will allow testing of a wide range
of hypotheses about faulting and earthquake generation, and the pursuit of
a scientific basis for earthquake hazards assessment and
prediction.
provide direct
information on the composition and mechanical properties of faulted rocks,
the nature of stresses responsible for earthquakes, the role of fluids in
controlling faulting and earthquake recurrence and the physics of
earthquake initiation and growth. Drilling, sampling, downhole
measurements and long-term moni- toring will allow testing of a wide range
of hypotheses about faulting and earthquake generation, and the pursuit of
a scientific basis for earthquake hazards assessment and
prediction.