Introduction
Since JAVA was introduced to the world of web in 1995, it has dominated the web software market in a few years. From the beginning, it designed as a simple, object-oriented, distributed, interpreted, robust, secure, architecture neutral, portable, high-performance, multi-threaded, and dynamic language. Though it has devised well as a secure language, it also has some secure holes. This document touches the JAVA's secure model, security attacks and antidotes, and their related links.
Java Security Model
- What Applets Can't Do
- Read files on the client file system.
- Write file stop the client file system.
- Delete files on the client file system.
- Rename files on the client file system.
- Create a directory on the client file system.
- List the contents of a directory.
- Check to see whether a file exists.
- Obtain information about a file.
- Create a network connection to any computer other than the host from which it originated.
- Listen for or accept network connections on any port on the client system.
- Create a top-level window without an untrusted window banner any means including trying to read the system properties.
- Define any system properties.
- Run any program on the client system.
- Make the Java interpreter exit.
- Load dynamic libraries on the client system.
- Create or manipulate any thread that is not part of the same ThreadGroup as the applet.
- Create a ClassLoader.
- Create a SecurityManger.
- Specify any network control functions.
- Define classes that are part of packages on the client system.
- Three-Pronged Defense
- Byte Code Verifier
- Class Loader
- Security Manager
- How Safe Are Applets?
- Type Safety
Java introduced several security protection models to prevent from potential attacks. To get this protection, it does not allow some functions through network loading and had three-pronged defense structure.
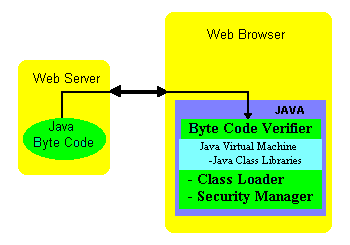
The verifier checks byte code at a number of different levels. more->
The Applet Class Loader determines when and how an applet can add classes to a running Java environment. more->
The Security Manager restricts the ways an applet uses visible interfaces. more->
- The Java language is designed to enforce type safety. This means that programs are prevented from accessing memory in inappropriate ways. Java uses static type checking to improve performance.
problem:It is too complicated. If an error occurred, it would be crucial hole in Java's type safety.
Serious Holes
- Jumping the Firewall.
- Tricks Java into treating the attacker's applet as trusted code.
- A buf in the Java byte code Verifier and a flaw in the class-loading mechanism.
- A Flaw in Java's Implementation of Sockets
- A flaw in the implementation of the Java interpreter. Netscape Navigator 2.02 and Microsoft Internet Explorer 3.0beta1 -> Fixed in Netscape Navigator 3.0beta3 and Microsoft Internet Explorer 3.0beta2
- You're not my type.
- A flaw in Java's implementation of array types.
- Casting Caution to the Wind.
- A flaw in Microsoft's Java implementation. - allowed code in an attack applet to become a member of a security-critical Java package.
Netscape Navigator 2.0 -> Fixed in Netscape Navigator 2.01
Netscape Navigator 2.01 -> Fixed in Netscape Navigator 2.02
Netscape Navigator 2.01 -> Fixed in Netscape Navigator 2.02
Netscape Navigator 3.0beta3 -> Fixed in Netscape Navigator 3.0beta4
Netscape Navigator 3.0beta5 -> Fixed in Netscape Navigator 3.0beta6
Netscape Navigator 3.0beta5 -> Fixed in Netscape Navigator 3.0beta6
Microsoft Internet Explorer 3.0beta3 -> Fixed in Microsoft Internet Explorer 3.0beta4
Malicious Applets
A malicious applet is any applet that attacks the local system of a Web surfer using one of the three less serious classes of attacks.
- Forge mail from a user to whomever the evil applet's author chooses saying whatever they wish while masquerading as the user.
- Steal CPU cycles to perform their own work while user's legitimate processes languish.
- Crash user's local system by using all available system resources.
- Hotile Applets Home Page
Antidotes
- High-level concerns:
- Programming Language Issues
- Formal Analysis
- Applet Logging
- Trust Models
- Distributed Nature of the Security Model
- Implimentaion versus Specification
- A Screening and Certification System for Untrusted Java Applets
- Decompilation
- Trusted Dialogs
- Guidelines for Java Users
- Know what Web sites a user is visiting.
- Know Java envionment.
- Use up-to-date browsers with the latest security updates.
- Keep a lookout for security alerts.
- Apply drastic measures if user's informations is truly critical.
- Assess a user's risks.
- Current Commercial Solutions
- Netscape's Server Solution
- Netscape Navigator 4.0
- Microsoft's Internet Explorer 4.0
Public variable should be avoid to use because it can be overwritten by an applet that has come across the network.
Packages in Java are too weak. A variable or method can be declared as accessible to classes within the current package, but there is no alternative way to control what sorts of other classes can access the variable.
Java's implementation of byte code is not optimal.
Any questions of provability are compounded by having two languages with separate semantics to understand (Java source and Java byte code). Formal verification invloves proving, in much the same way that a theorem is proven in mathematics.
Keep track of what Java does on users's machine.
The trusted and known web site can be no fear to use Java applets.
Java implementations are run on the distributed system and it is hard to verify. If all of the security-critical functions were collected together in one place, it would be easy to analyze.
To prevent the Class Loader attack, the new Java specification declares that the VM must remember the answers given by each Class Loader. (Java Development Kit 1.1 implemented this specification.)
It turns out that one of the side-effects of Java byte code's clarity is that byte code is very easy to decompile.
Mocha, the Java Decompiler
Trusted dialogs like file access would provide an important monitoring and feedback mechanism to Java users.
-
Encripted the sensative data and Signed Applets.
Java Security FAQ Links
- Frequently Asked Questions - Java Security(JavaSoft)
- Princeton's FAQ
- The World Wide Web Security FAQ
- CERT Alerts
Reference
-
Java Security: Hostile Applets, Holes, & Antidotes, Gary McGraw & Edward Felten, 1997, John Wiley & Sons