


Next: Properties of Gaussian
Up: 1: Basic Definitions
Previous: 1.3Continuous Distributions General
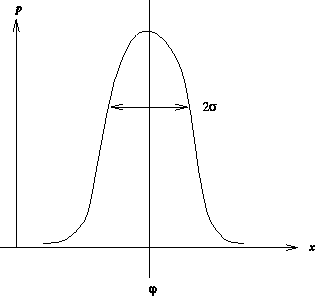
- (b) Another important example is

- This is the probability density of the normal or Gaussian
distribution---so called because it was first discussed by de Moivre in
1733.
Geoffrey Fox, Northeast Parallel Architectures Center at Syracuse University, gcf@npac.syr.edu


