


Next: Central Limit Theorem
Up: 1: Basic Definitions
Previous: Moment Generating Function
- Expanding the exponential in definition of
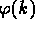 give
give
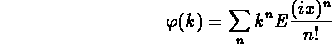
- where E is the expectation or mean value.
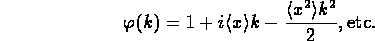
- For a Gaussian distribution
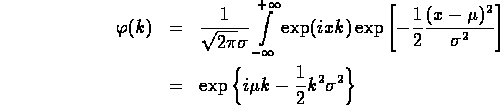
- EJDRS define the Cumulant as

- I have never used this! Note that
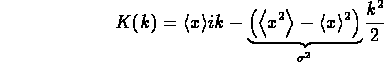
- i.e., as
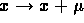 only shifts K by additive
constant
only shifts K by additive
constant 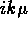 , we only find ``central'' moments for coefficients of
, we only find ``central'' moments for coefficients of
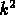 and above.
and above.
Geoffrey Fox, Northeast Parallel Architectures Center at Syracuse University, gcf@npac.syr.edu
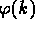 give
give
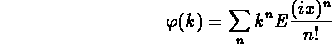
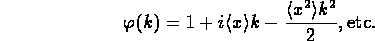
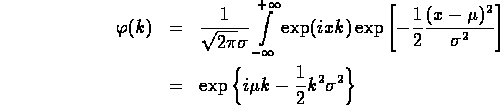

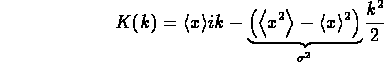
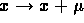 only shifts K by additive
constant
only shifts K by additive
constant 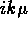 , we only find ``central'' moments for coefficients of
, we only find ``central'' moments for coefficients of
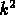 and above.
and above.
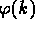 give
give
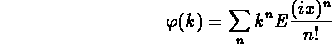
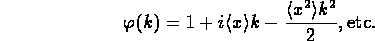
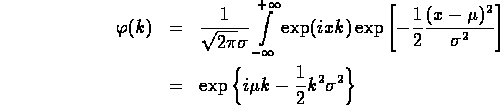

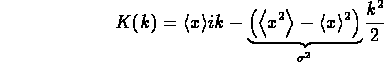
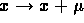 only shifts K by additive
constant
only shifts K by additive
constant 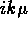 , we only find ``central'' moments for coefficients of
, we only find ``central'' moments for coefficients of
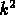 and above.
and above.