


Next: Central Limit Theorem
Up: 1: Basic Definitions
Previous: Extension of Central
- Then, the new Central Limit Theorem states that the pair (F,G)
is asymptotically a (two-dimensional) Gaussian distribution with
probability distribution
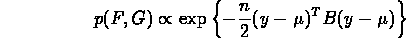
- where we have lapsed into a vector notation:
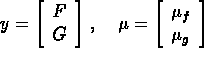 and matrix
and matrix 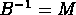 .
.
- Proof: Just as in ordinary central limit theorem, except
you consider two-dimensional characteristic function
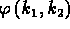 .
.
- This extension is important as it allows you to use correlations
between functions calculated from the same data (observations).
Geoffrey Fox, Northeast Parallel Architectures Center at Syracuse University, gcf@npac.syr.edu
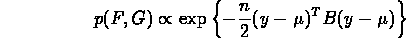
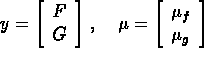 and matrix
and matrix 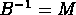 .
.
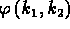 .
.
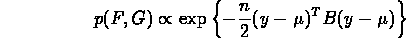
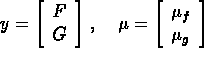 and matrix
and matrix 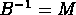 .
.
 .
.