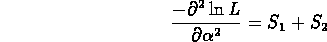Next: Derivative Calculation for
Up: 4: Minimization
Previous: Derivative Formalism for
- Let's do the same thing for maximum likelihood method.
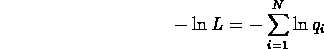
- where
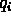 are probability of our
are probability of our 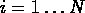 events.
events.
- Assume
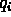 are normalized
are normalized 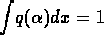 as in
Equation (25).
as in
Equation (25).
- This normalization is crucial but even when it does
not seem to be true as in our subtle modifications in Section 4.3 with
the ``generalized'' maximum likelihood method, one can easily modify
the analysis, and show it is still valid.
- We get in normalized
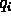 case,
case,
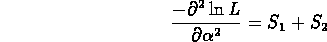
- with

Geoffrey Fox, Northeast Parallel Architectures Center at Syracuse University, gcf@npac.syr.edu
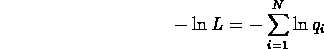
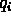 are probability of our
are probability of our 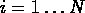 events.
events.
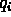 are normalized
are normalized 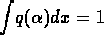 as in
Equation (25).
as in
Equation (25).
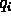 case,
case,
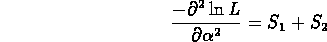

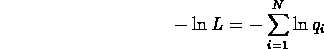
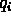 are probability of our
are probability of our 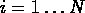 events.
events.
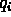 are normalized
are normalized 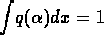 as in
Equation (25).
as in
Equation (25).
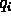 case,
case,