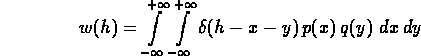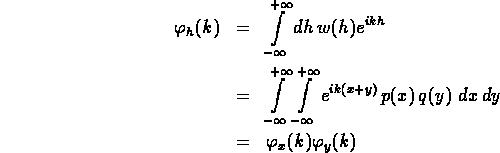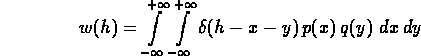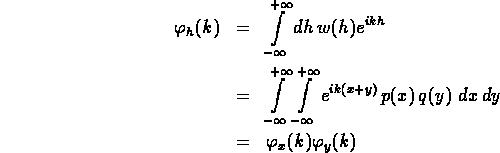Next: Moment Generating Function
Up: 1: Basic Definitions
Previous: 1.7Leading Up to
- In an important application of moment generating functions, put
h=x+y where x and y are independent.
- From joint probability distribution, it follows that the distribution
density of h is
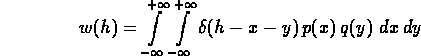
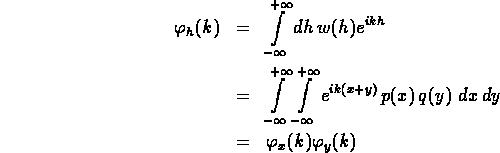
- So characteristic functions multiply for addition of two
independent random variables.
- This result can obviously be extended to sum of n independent
random variables.
Geoffrey Fox, Northeast Parallel Architectures Center at Syracuse University, gcf@npac.syr.edu