


Next: The TexasSyracuse
Up: No Title
Previous: Methods to try
The inner boundary is a problem for several reasons:
- We will excise the points inside the apparent horizon.
- We would like to excise the points inside the event horizon.
The problem is that the event horizon is only known at
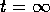 .
Thus, we need a way to exclude the singularity of the hole.
.
Thus, we need a way to exclude the singularity of the hole.
- The apparent horizon is found by looking for Trapped surfaces.
This breaks down into solving a very difficult elliptic equation.
- When the hole moves in the computational domain, coordinate points
that were previously excised will now appear
inside the computational
domain.
Many groups have explored special ways to difference around the holes
(causal differencing).
A new formalism, J. York, the ``hyperbolic'' formalism was developed such that
relativist would not have to worry about the gauge freedom.
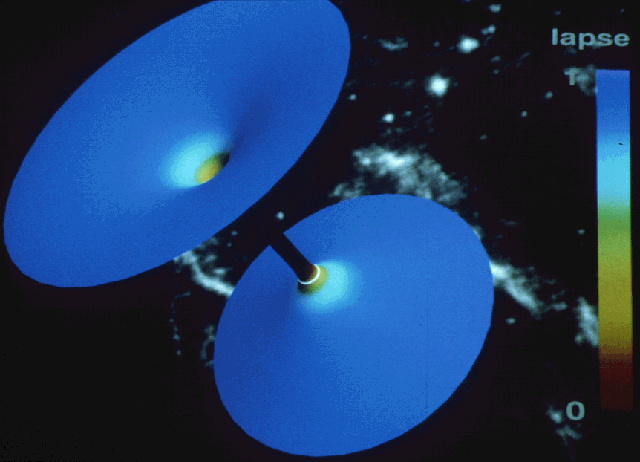
Below is an embedding of a curved black hole space in a fault
Euclidian space at t=4.0M with maximal slicing.
The long cylinder is formed by the avoidance of the central
singularity. The color represents how fast clocks record proper
time (red for slow, blue for fast).
Background is the
Cygnus region Cygnus X-1 (x-ray source) is a possible candidate
for a black hole. Picture from L. Smarr, D. Hobill, D. Bernstein;NCSA.
Scott Klasky
Wed Feb 28 10:19:33 EST 1996
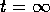 .
Thus, we need a way to exclude the singularity of the hole.
.
Thus, we need a way to exclude the singularity of the hole.
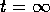 .
Thus, we need a way to exclude the singularity of the hole.
.
Thus, we need a way to exclude the singularity of the hole.
