


Next: Correlated Observations in
Up: 3: Estimation of
Previous: Mean and Standard
- Thus, if value of
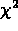 is many (say >3) standard deviations
away from its mean, then the theoretical form is in doubt.
is many (say >3) standard deviations
away from its mean, then the theoretical form is in doubt.
- The usual maximum likelihood method does not have this
advantage: remember L was unnormalized and so its value had no
significance for the goodness of fit.
- This is quite a difficult problem and an elementary discussion is
given in MacDonald notes, page 14 onwards.
- The only way to get a feeling for
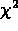 is to use it: so I
won't dwell here on the important techniques used to minimize
is to use it: so I
won't dwell here on the important techniques used to minimize 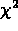 to get good theoretical parameters and estimate errors in the same. We
will come back to this later in the notes.
to get good theoretical parameters and estimate errors in the same. We
will come back to this later in the notes.
- Mathews and Walker solve the simplest problem, i.e.,
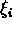 are
linear in theoretical parameters.
are
linear in theoretical parameters.
- We do an example of this below.
- Bevington or similar book should be read before tackling a real
problem.
Geoffrey Fox, Northeast Parallel Architectures Center at Syracuse University, gcf@npac.syr.edu
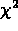 is many (say >3) standard deviations
away from its mean, then the theoretical form is in doubt.
is many (say >3) standard deviations
away from its mean, then the theoretical form is in doubt.
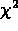 is to use it: so I
won't dwell here on the important techniques used to minimize
is to use it: so I
won't dwell here on the important techniques used to minimize 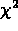 to get good theoretical parameters and estimate errors in the same. We
will come back to this later in the notes.
to get good theoretical parameters and estimate errors in the same. We
will come back to this later in the notes.
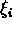 are
linear in theoretical parameters.
are
linear in theoretical parameters.