Table of Contents for N Body Problems using Data parallel Approach
CPS 615 1998 Update for N body Simple Algorithm with Data parallel F90/HPF
- See message parallel solution in N Body Problems using Message Parallel Approach
Simulation Track
Data Parallel Module on ODE's and Particle Dynamics
February 20, 1998
2
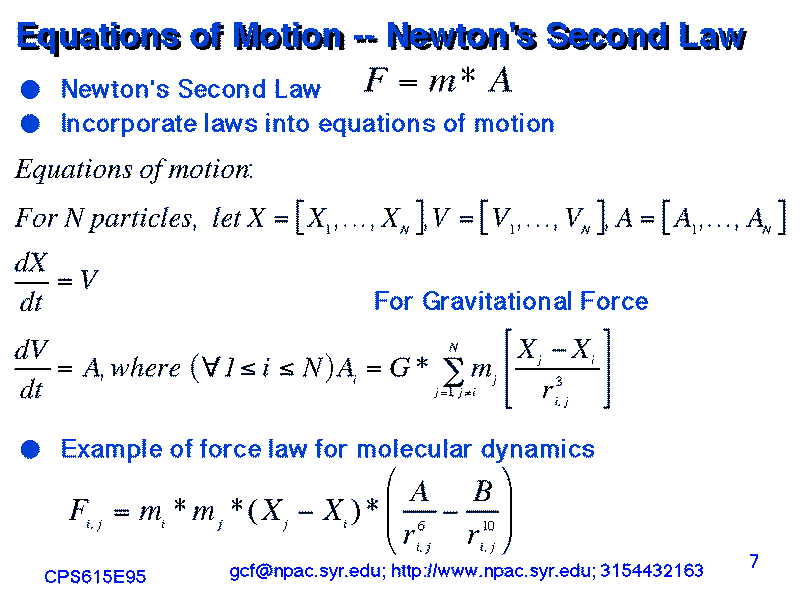
Particle Dynamics as applications
3
4
5
6
7
ODE Solution Techniques
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
Setup of N Body Problem
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
Simple Data Parallel Approach
33
34
35
36
37
Problems with Simple Method
38
39
Data Parallel Pipeline Algorithm
40
taking 1/2 the time for iterations over force computation
41
42
43
44
45
46
Performance Issues
47
48
49
One Dimensional System Dimension
50
HPF Version
51
52
53
References
54