Table of Contents for CPS615 - Overview of Computer Architectures
A Brief Discussion of Computer Architectures
1
2
3
Technologies of Relevance
4
5
6
7
Commodity Driving Forces
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Parallel Computing Architectures
18
19
20
21
Performance Issues
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
Sequential Computer Architecture
37
Pipelining
38
39
40
41
Caches
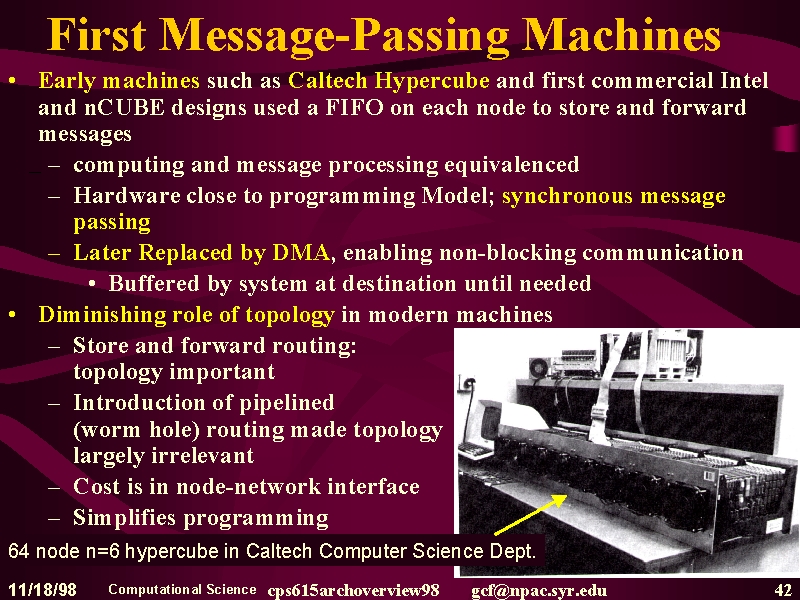
42
43
44
45
46
47
Cray T3E as an Example of a Cache
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
Vector Architecture
57
58
59
60
Parallel Memory Structure
61
62
63
64
Parallel Control Structure
65
MIMD Architectures
66
67
68
69
70
71
Parallel Computing Cache Issues
72
73
74
Origin 2000 as an Example of Cache Coherence
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
SIMD Architectures
82
83
84
85
86
Metacomputers
87
88
89
90
Special Purpose Devices
91
92
93
94
95
Granularity
96
97
Parallel Computer Networks
98
99
100
101
Network Performance
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
Architectures according to Culler
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
Intel SMP
119
Sun E10000 as Example of UMA Commodity System
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
Current Near Term Trends
128
129
130
Emerging Architectures MTA and COMA
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
Application Motivation for PetaFlops
145
146
147
148
149
The 3 classes of PetaFlop Designs
150
151
152
153
154
The Processor in Memory Design
155
156
157
158
Exotic Technology: Quantum Computing
159
160
161
Exotic Technology: Superconducting Technology
162
163
164